Infertility tests are important for us to evaluate your treatment options and fertility success. A combination of these tests and all the information gathered about you is used to develop a customized treatment plan.
Female Infertility Tests
Day 3 Tests
Day 3 tests are performed on the second, third, or fourth day of your menstrual cycle.
These tests provide important information about your likelihood of responding to egg-stimulating drugs. They measure hormone levels in your blood to assess reproductive health and ovarian reserve.
Female fertility is closely related to hormonal balance. Hormones initiate egg development and determine the appropriate timing for ovulation. Furthermore, they determine how the embryo will implant in the uterus. For good eggs, good embryos, and successful implantation, hormonal balance is crucial, and proper timing, along with compatibility between the embryo and the uterus, is essential.
Therefore, to assess female fertility, we primarily rely on various hormonal tests. A range of different hormones affect fertility health.
These hormones include;
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) that stimulates the ovaries
- Luteinizing hormone (LH) that stimulates the release of eggs from the ovaries
- Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) indicating ovarian reserve
- Estradiol and Progesterone which prepare the endometrial lining for implantation
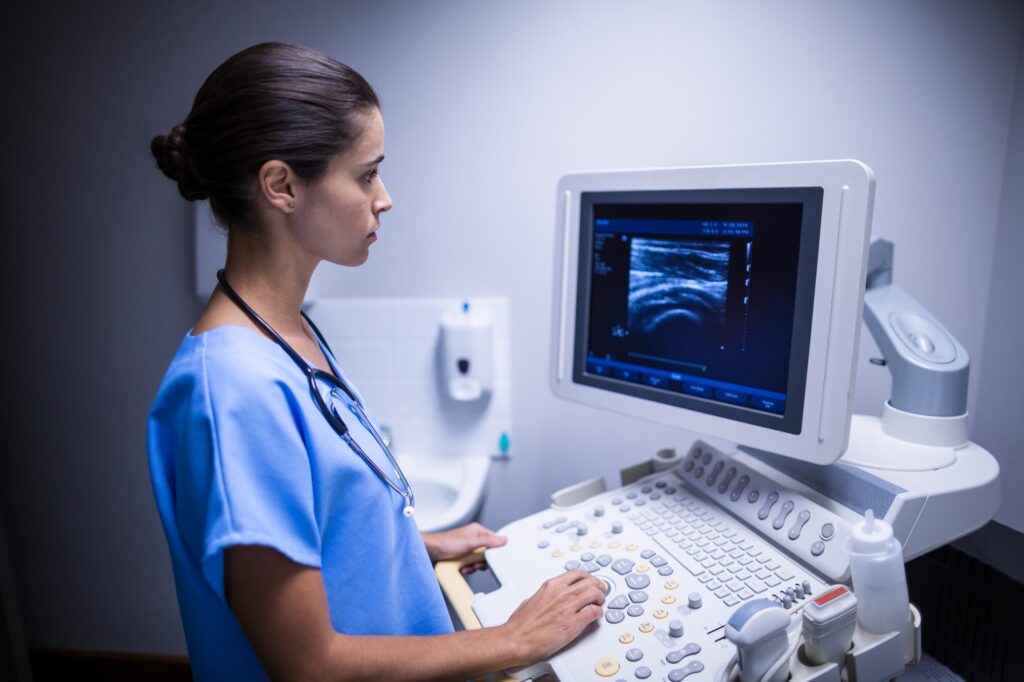
Ultrasound
Traditional ultrasound tests allow the evaluation of the health of your ovaries, uterus, and follicles. Transvaginal ultrasound can assess small follicles in the ovaries (called antral follicles).
To obtain an adequate number of eggs from the ovaries, the total number of antral follicles should be around 10. Ultrasound is also an important test tool for evaluating the thickness and shape of the uterine lining (endometrium) during the ovulation period.
Hysterosalpingogram (HSG) Test
We use an X-ray test called HSG to examine the walls of the uterus and fallopian tubes. This test allows your doctor to see if your fallopian tubes are open and also assess the shape of your uterus.
The HSG test involves placing a small catheter into the uterus and injecting a fluid (contrast material) that can be seen on the X-ray screen. The entire procedure takes about 15 minutes and is usually performed between the 5th and 12th days of your menstrual cycle, before ovulation.
Sonohysterogram (SIS) Test
This simple ultrasound test examines the uterine cavity for abnormalities such as polyps or fibroids. It is performed between the 5th and 12th days of the cycle and lasts about 10 minutes. The SIS test can confirm that the inside of the uterus is normal. The uterus is filled with fluid through a thin catheter inserted via the cervix, and the uterine cavity is examined with ultrasound during this process.

Male Infertility Tests
Testing the male partner’s sperm sample allows us to gather important information about the reproductive history, medical background, and lifestyle. A semen analysis test provides detailed information about fertility issues that an individual or couple might face.
Semen Analysis Process
A semen sample must be collected to evaluate the sperm. This process may be uncomfortable for many men, and therefore, sample collection can be done in a private collection room at our center. The results of this test are provided quickly after our embryologists measure the following characteristics, which are crucial for egg fertilization and pregnancy:
Semen Volume
Shows how many milliliters of semen are produced. Low volumes may indicate obstruction or dysfunction in the seminal vesicles or prostate. The volume should be greater than 2 mL.
Semen Motility
Shows how many motile sperm are present. This characteristic allows sperm to combine with the egg in the fallopian tube. Generally, at least 50% of sperm should be motile.
Semen Morphology
Refers to the actual shape of the sperm. If more than 50% of the sperm have abnormal shapes, male fertility is affected.
Semen Concentration
Shows how many millions of sperm are produced per milliliter. Low counts may indicate that sperm is being blocked from exiting or that the testes are not producing sperm properly.
Sperm Appearance
The color of sperm may indicate the presence of blood or side effects from medications used.

 EN
EN TR
TR
